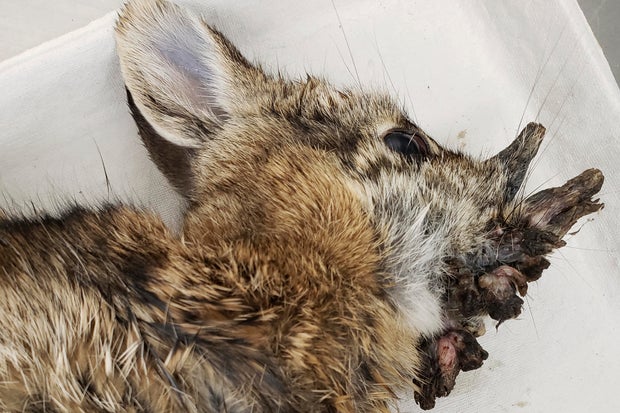
A group of rabbits in Colorado, grotes, horn-like growth may look directly from a low-budget horror film, but scientists say that there is no reason for this-only a relatively common virus in the live organisms.
The recently spotted cottons in Fort Colins are mostly harmless to infected ShopilomavirusWhich causes a wart -like growth that spreads from their face such as metastasizing horn.
Viral photos have inspired a fluff of unwanted surnames, including “Frankstein Banniz,” “demon rabbits” and “zombie rabbits”. But their grief is not new, in which the virus inspires ancient folklore and promotes scientific research about 100 years ago.
The virus influenced the centuries -old Jacquelop myth in North America, which explained an rabbit with anter or horns among other animal variations. The disease in rabbits also contributed to the knowledge of scientists about the relationship between viruses and cancer, such as human papillomavirus which is the cause cervical cancer.
Dr. Rachel Ruden/Iowa Department of Natural Resources AP
Among the rabbits, the virus was named Dr. Dr. Dr. Richard E was named after Shop, who discovered the disease in cottons in the 1930s.
The news about the view of the rabbit in Fort Colins, 65 miles of Denver, began to attract attention after spotting the residents around the city and posting pictures.
“It seems that these black quills or black toothpicks were sticking around her mouth,” Susan Mansfield, a fort colon’s resident, who saw one of the rabbits, Told 9news“I thought he would die during winter, but it did not happen. He came back in another year, and it increased.”
Kara Van Hos, a spokesman for Colorado Parks and Wildlife, told the associated press on Wednesday that the agency was receiving calls about rabbits seen in Fort Colins.
But he said that it is not uncommon to see infected rabbits, especially in summer, when the flea and ticks that spread the virus are the most active. The virus can spread from rabbit to rabbit, but not in other species, including humans and pets, he said.
Rabbit papilloma is similar to human HPV-inspired tumor, according to an article National library of medicineAccording to a recent report, human papillomavirus has been associated with skin cancer.
Van Hos said that Vikas comes from warts, but can look like horns. The increase does not harm rabbits until they grow on their eyes or mouth and interfere with eating. He said that the immune system of rabbits is capable of fighting the virus and, once they do, the growth will disappear, she said.
Agency notes The disease is more severe in domestic rabbits than wild rabbits and should be treated by a veterinarian.
Colorado cottles are home to three separate species of rabbits – mountain cottles, desert cottons and eastern cottles. Colorado Park and Wildlife say, “The species differ mostly from the colors and” except for the habitat and geographical location “is difficult or impossible to distinguish the ground.”